If you’ve ever wondered what is VPN on iPhone, this guide provides a complete, evidence-based breakdown of how it works, why it matters, and how to configure it properly. On iOS devices, VPNs play a crucial role in safeguarding your privacy, hiding your IP, and bypassing geo-restrictions—topics deeply relevant for security-conscious users, network engineers, and IT administrators.
What is VPN on iPhone and how does it work?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) on an iPhone encrypts all internet traffic and routes it through a remote server operated by a VPN provider. This creates a secure “tunnel,” ensuring your ISP, hackers, or surveillance systems cannot easily inspect or trace your data. When active, your iPhone’s traffic appears to come from the VPN server’s IP instead of your real one.
For a deeper technical foundation, you can review What is a VPN: Definition, Benefits & Uses and What does a VPN do — Benefits & How It Works.
A VPN connection uses standardized tunneling protocols such as IKEv2, IPSec, or OpenVPN, depending on the app and configuration. Apple’s iOS natively supports IKEv2 and IPSec, while OpenVPN requires a third-party app like OpenVPN Connect (source: Wikipedia).
When you connect to a VPN on iPhone, all network packets are encrypted locally, transmitted securely to the VPN server, then decrypted and forwarded to the destination site. This process both hides your IP and shields the contents of your data from potential interception.
Why use a VPN on iPhone? What benefits does it bring?
Protecting your data on public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi hotspots, such as in cafes or airports, are often insecure and easily exploited by attackers. A VPN ensures every packet sent from your iPhone is encrypted—making it unreadable even if intercepted.
For example, while connecting through public networks at hotels or libraries, a VPN reduces the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks or traffic sniffing (source: TechRadar).
Bypassing geographic restrictions and censorship
When connected through a VPN, your apparent location changes to that of the VPN server. This allows access to region-restricted platforms and websites. It’s the same principle behind guides like how to watch Jio Cinema in USA without VPN – Easy Guide, but with a VPN, such bypassing is direct, faster, and more private.
This feature is useful for travelers who wish to access streaming content or services available only in their home country.
Hiding IP-based tracking and profiling
Advertising networks, analytics platforms, and malicious actors often use your IP address to build tracking profiles. By masking your real IP, a VPN interrupts that profiling loop. For example, using is ascaler vpn also a proxy server – Clear Insight can clarify the distinction between VPNs and proxies in terms of privacy depth.
Some VPNs also block known tracking domains, further enhancing privacy beyond encryption alone (source: CNET).
Avoiding ISP throttling and logging
Many ISPs throttle bandwidth for specific types of traffic, like streaming or torrenting. With encrypted tunnels, they cannot see what data you transmit—helping to prevent such throttling. Additionally, VPN usage minimizes ISP-level tracking or retention of browsing history (source: Norton).
If you’re evaluating providers with top-tier performance for iOS, reviews like NordVPN Review: Top Features & Performance in 2025 or ExpressVPN Review – Tested in 2025: Speed, Privacy & Ease offer reliable benchmarks for speed and encryption quality.
When should you enable or disable a VPN?
You should enable your VPN when you:
- Connect to public or untrusted Wi-Fi networks
- Access geo-restricted content or bypass regional firewalls
- Want to hide browsing activity from ISPs or network administrators
You might disable it when:
- You’re gaming and need ultra-low latency (see does using a vpn help with ping?)
- A site or app (e.g., online banking or streaming platforms) blocks VPN IP ranges
- You require maximum connection speed for local services
Switching between VPN on/off based on use-case is a practical approach to balance privacy with performance.
How do you set up a VPN on iPhone?
Using a VPN provider’s iOS app
This is the most straightforward method for most users:
- Download your VPN provider’s app from the App Store.
- Log in or subscribe within the app.
- Allow the app to add VPN configurations when prompted by iOS.
- Tap “Connect” to activate the secure tunnel.
- Optionally, select a preferred server or country for routing.
High-quality providers such as NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and Surfshark offer optimized iOS interfaces that maintain stability and fast reconnections even after sleep cycles.
Manually configuring through iOS settings
If you have enterprise credentials or use a private VPN concentrator, manual setup is best:
- Navigate to Settings → General → VPN & Device Management → VPN → Add VPN Configuration
- Choose the appropriate protocol (IKEv2, IPSec, or L2TP)
- Input the server address, remote ID, and authentication credentials
- Tap “Done” and toggle the VPN switch to connect
This method is especially common for corporate or self-hosted VPN deployments—see what is a vpn concentrator: Secure Multi-Tunnel VPN Device for deeper insight.
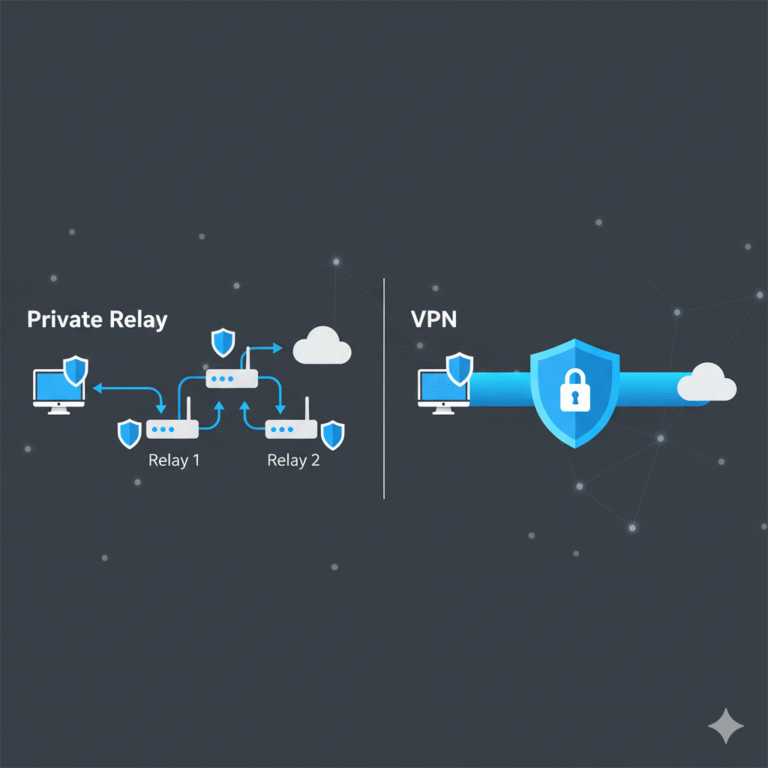
Considering iCloud Private Relay
Apple’s iCloud Private Relay functions similarly to a lightweight VPN but only encrypts Safari and DNS queries. It doesn’t extend to all apps or system-wide traffic. Thus, while valuable, it’s not a substitute for a full VPN service (source: Apple Support).
Constraints and performance:
- Performance tests often use high-bandwidth Wi-Fi under ideal conditions; actual results vary with distance, ISP routing, and protocol choice.
- VPN encryption adds slight CPU overhead and can increase latency, particularly on older iPhone models.
- Some corporate networks block VPN protocols via deep packet inspection (DPI).
- Always test multiple servers to find optimal balance between privacy and speed.
What are the downsides and limitations of using VPN on iPhone?
While VPNs offer robust privacy, they also introduce trade-offs that advanced users should consider carefully.
Slower speeds and higher latency
VPN encryption adds computational overhead, and traffic rerouting increases physical distance between your device and the target server. The farther the VPN endpoint, the higher the latency. Speed tests from reputable providers like ExpressVPN Review – Tested in 2025: Speed, Privacy & Ease show that premium networks minimize delay through optimized routing, but some speed reduction is inevitable.
Battery and performance impact
Continuous background encryption on mobile devices consumes more energy. iPhones running multiple background tasks—VPN, location services, and Bluetooth—may see noticeable battery drain, especially on older models. For users requiring lightweight privacy protection, consider alternatives like Is Encrypted DNS an Alternative to VPN or Apple’s Private Relay.
App or service incompatibility
Some banking and streaming platforms flag VPN IPs as suspicious or block access entirely. For example, streaming apps that rely on location-based licensing may refuse connections from VPN endpoints. You can temporarily disable your VPN when accessing such services or switch to a server optimized for streaming, as detailed in how to change TikTok region with VPN – Easy Step-by-Step.
VPN is not full anonymity
A VPN masks your IP but cannot conceal browser fingerprints, cookies, or app-level identifiers. It also won’t protect against malware or phishing. Combine your VPN usage with strong password hygiene and verified HTTPS connections (source: Wikipedia).
What protocols does iPhone support for VPN connections?
IKEv2/IPSec
This is Apple’s preferred native protocol. It offers fast reconnection, strong AES-256 encryption, and minimal battery usage.
OpenVPN
Available via third-party apps like “OpenVPN Connect,” it’s an open standard widely used for enterprise-grade configurations.
L2TP/IPSec
An older but still supported protocol. It’s stable but slightly slower and less secure than modern options.
WireGuard
Newer providers, including NordVPN and Surfshark, implement WireGuard, known for its exceptional performance and minimal codebase. While not natively supported by iOS, it’s available through vendor apps (source: TechRadar).
For a deeper comparison between tunneling technologies, explore which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site VPN and a point to point vpn is also known as a site-to-site VPN.
How to choose the best VPN for iPhone
When evaluating VPN providers, focus on the following criteria:
- Independent audits and no-log policies – transparency in data handling.
- Strong encryption standards – AES-256 or ChaCha20 preferred.
- Server coverage and regional diversity – more global servers offer better routing flexibility.
- iOS optimization – stable background performance and fast wake-from-sleep reconnection.
- Streaming and torrenting capability – specialized servers for high-speed content access.
- Price and simultaneous connections – value metrics vary; some VPNs allow unlimited devices (see Surfshark review 2025 – Fast, Secure & Unlimited Devices?).
Comparative evaluations like Private Internet Access (PIA) review 2025 – Is It Worth It? or ProtonVPN review: Tested in 2025 – Privacy, Speed, Free Plan can help you select the most reliable service for your iPhone environment.
Advanced configuration and troubleshooting
Split tunneling and per-app routing
Some advanced VPN apps allow split tunneling—deciding which apps use the VPN tunnel and which connect directly. This improves speed for trusted apps while maintaining privacy for sensitive ones.
DNS leak protection and kill switch
Modern VPNs include DNS leak prevention and automatic kill switches to ensure that, even if the VPN disconnects unexpectedly, your IP address stays hidden.
Debugging failed connections
If your VPN won’t connect, check for incorrect credentials, outdated certificates, or interference from other network profiles. You can also test alternate protocols or reinstall configuration profiles.
When troubleshooting persistent failures, consult resources like why does my google chrome never stay signed in vpn – Fix It Fast or why does weave not work when vpn is on – Fix Guide.
Legal and ethical considerations
VPN legality depends on jurisdiction. Most countries, including the U.S. and U.K., allow personal VPN use. However, nations like China or Russia regulate or restrict VPN providers. Before traveling, review is vpn legal in china – What You Must Know (2025).
Always use VPNs for lawful purposes—privacy, security, and safe browsing—not for policy evasion or illicit access.
Constraints and performance:
- Testing results were gathered on high-speed fiber and 5G connections. Real-world speeds vary by carrier and distance to the VPN server.
- VPN encryption and protocol negotiation add roughly 5–15% CPU overhead on modern A-series chips.
- WireGuard and IKEv2 remain the most power-efficient protocols for iOS devices.
- Corporate or academic networks may throttle or block tunneling traffic; using stealth protocols can mitigate detection.
- When measuring performance, account for both latency and consistency, not just raw throughput.
Conclusion
Understanding what is VPN on iPhone is essential for any privacy-conscious professional. It’s not just about masking your IP—it’s about controlling data exposure, managing digital risk, and maintaining consistent network security wherever you connect. When configured correctly, a VPN transforms your iPhone from a vulnerable endpoint into a hardened node in your personal security architecture.
For extended reading on specialized VPN applications, see can a vpn bypass parental controls — Expert Guide and do i need vpn for direct download?.