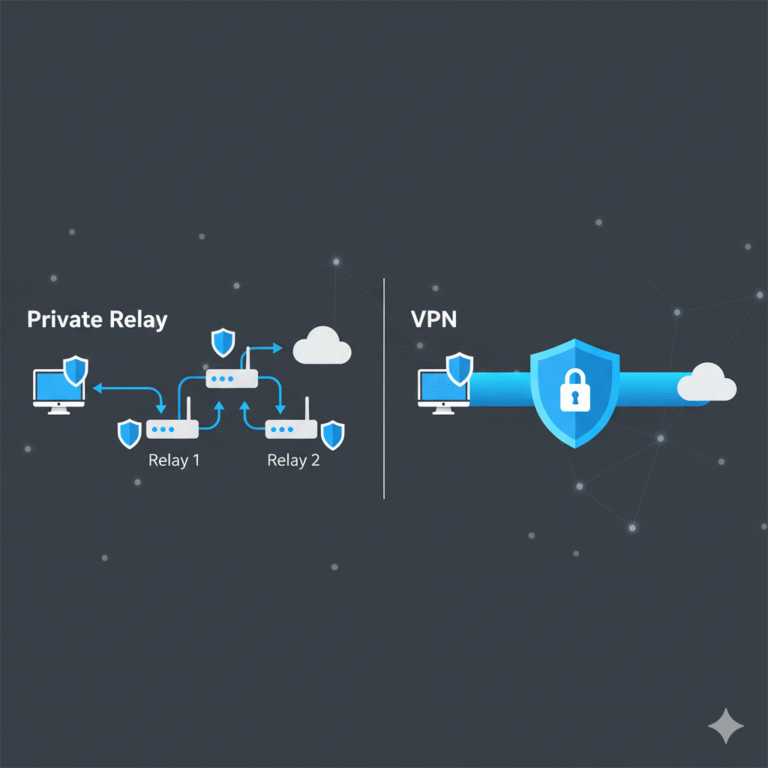
If you’ve ever asked yourself what is my ip address vpn, you’re exploring one of the most essential privacy checks any VPN user can perform. Verifying your visible IP ensures that your VPN actually hides your real location and identity online. This guide explains how to confirm your public IP while connected to a VPN, how to detect potential leaks, and what to do if your VPN isn’t performing as expected.
What Is a VPN and How Does It Affect Your IP Address?
A VPN — short for Virtual Private Network — encrypts your data traffic and routes it through a secure tunnel to a remote server. As a result, websites and services see the VPN server’s IP address instead of your real one (source: Wikipedia). This helps you maintain online privacy, bypass censorship, and prevent ISPs or advertisers from tracking your browsing activity.
If you’re new to the concept, check this detailed guide: What is a VPN: Definition, Benefits & Uses.
You can also explore how VPNs differ from proxies in this breakdown: is ascaler vpn also a proxy server – Clear Insight.
While VPNs are powerful, they’re not flawless. A misconfiguration, weak encryption, or an accidental “leak” can expose your real IP, revealing your identity or location. That’s why testing what is my ip address vpn is crucial to verifying your VPN’s reliability.
Why You Should Check “what is my ip address vpn”
There are several reasons to verify your VPN IP address:
- Prevent IP leaks: Even with a VPN enabled, your device might still broadcast your real IP via WebRTC or IPv6 leaks.
- Avoid DNS leaks: If your DNS queries bypass the VPN tunnel, your ISP can still see what websites you visit.
- Ensure correct server assignment: Sometimes, VPNs connect you to the wrong region due to internal routing or load balancing.
To learn more about server behavior, read: which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site vpn.
Testing your IP after connecting helps confirm whether your VPN is functioning correctly and your true IP is fully hidden.
What Methods Can You Use to Check “what is my ip address vpn”?
Here are four trusted approaches used by cybersecurity experts and network engineers:
- Use a reliable IP lookup service
Visit an IP lookup or VPN detection site like IPQualityScore’s VPN/IP check tool to instantly see your visible IP, ISP, and whether the address is flagged as a VPN or proxy. - Run browser-based leak detection tools
Use advanced testing platforms such as BrowserLeaks or BleepingComputer’s VPN IP check guide for detailed WebRTC, IPv6, and DNS leak results. These reveal if your browser leaks identifiable information outside the VPN tunnel. - Compare your IP before and after connecting
- Disconnect the VPN and check your IP.
- Connect to your VPN and test again.
- If your IP changes to the VPN server’s address, your connection is working correctly. If it doesn’t — or if your DNS still shows your local ISP — a leak exists.
- Check routing and logs (advanced users)
Experienced users can inspect routing tables or connection logs with tools likenetstat,ipconfig, ortracerouteto ensure all traffic flows through the VPN interface.
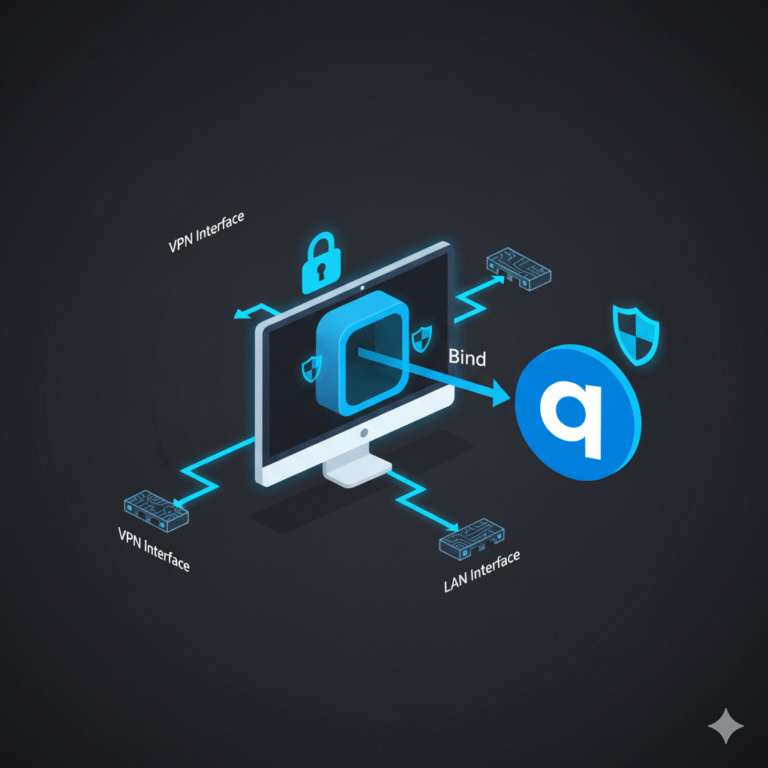
For additional guidance on setting up secure VPN connections, explore: how to bind qbittorrent to vpn for secure torrenting.
Common Causes of IP Leaks
Even reliable VPNs can suffer from configuration issues. The most frequent causes include:
- WebRTC revealing local IP addresses in browsers like Chrome or Firefox
- IPv6 traffic bypassing the VPN tunnel
- Custom DNS settings that override the VPN’s DNS servers
- VPN kill switch not properly configured
- Split tunneling that excludes certain apps or connections
To learn more about how protocols and configurations affect performance, see what is a vpn concentrator: Secure Multi-Tunnel VPN Device.
How to Fix a Leak Once Found
- Disable WebRTC in your browser or use privacy extensions to block it.
- Disable IPv6 if your VPN doesn’t support it.
- Force DNS queries through the VPN by using provider-assigned DNS servers.
- Enable your VPN’s kill switch to block traffic when the tunnel drops.
- Avoid split tunneling unless you fully understand its security implications.
You can also compare leading VPNs’ leak protection and performance in this in-depth review: NordVPN Review: Top Features & Performance in 2025.
Constraints and performance:
Testing VPN visibility and IP leaks involves several real-world variables:
- Network variance: ISP routing, firewalls, and NAT types affect test accuracy.
- Regional inconsistencies: VPN servers may route IPv6 or DNS traffic differently per country.
- Tool discrepancies: Some IP checkers cache old data or use inconsistent DNS resolvers.
- Performance trade-offs: Stronger encryption and multi-hop routes can reduce speed.
Practical guidance: Always perform multiple tests across different devices and networks. If your visible IP remains constant across checks, your VPN is functioning properly. Otherwise, consult your provider or switch to a more reliable service like ExpressVPN Review – Tested in 2025: Speed, Privacy & Ease.
Conclusion
Understanding what is my ip address vpn is essential to maintaining true online privacy. Regular IP and leak testing ensure your VPN performs as promised — encrypting data, masking your location, and preserving anonymity. Whether you’re streaming, gaming, or working remotely, knowing your VPN hides your real IP gives you peace of mind and control.
How Do VPN IP Checks Work Behind the Scenes?
When you use a VPN IP checker, it collects information from several sources to determine what your network reveals publicly. These sources typically include:
- Public IP lookup: identifies the IP address your requests originate from.
- Reverse DNS lookup: checks the hostname associated with the IP (often revealing whether it belongs to a datacenter or consumer ISP).
- Geo-IP databases: locate your IP geographically.
- ASN records: show which organization owns the IP block — most VPN IPs belong to datacenters or hosting providers.
By comparing these details, IP checkers decide whether your traffic likely comes from a VPN, proxy, or residential network.
For a deeper understanding of network mapping, you can read Does VPN Work With Ethernet — Secure Wired VPN Usage.
Can IP Leaks Affect Your Online Privacy or Access?
Yes. Even small leaks can have significant consequences:
- Privacy exposure: Your real IP can reveal your approximate location, ISP, and even organization.
- Access issues: If your VPN leaks your IP while you’re accessing geo-blocked services, streaming sites or platforms like Netflix may block your connection.
- Security threats: Persistent leaks can let ISPs or trackers correlate traffic to your real identity.
If you use your VPN to bypass content restrictions, make sure it’s functioning correctly. For example, users streaming international content can review this guide: how to watch jio cinema in usa without vpn – Easy Guide.
How to Verify if Your VPN Truly Hides Your Real Location
To confirm full protection, follow this test flow:
- Disconnect your VPN and record your IP using an external IP tool.
- Connect to your VPN and repeat the test.
- Check DNS, WebRTC, and IPv6 leaks via multi-layer testing tools.
- Inspect your routing and firewall rules if any test still shows your real IP or ISP.
If the IP doesn’t change or partial leaks occur, try another provider known for solid encryption and DNS handling. A detailed analysis is available in this comparison: AirVPN vs NordVPN: Which VPN Offers Better Security & Speed?.
Should You Use Free Tools or Paid VPN Leak Tests?
Free IP lookup services can show your basic IP, but premium leak test suites provide deeper insights like WebRTC, IPv6, and DNS detection. The best approach combines both:
- Free tools: quick for IP visibility.
- Advanced testing platforms: useful for verifying tunnel integrity and DNS behavior.
Reputable providers like ProtonVPN and CyberGhost VPN also offer internal IP-check dashboards for verification.
Constraints and performance:
VPN IP checks are influenced by multiple technical and environmental factors:
- Testing region: Latency or routing differences may alter visible results.
- Browser or OS limitations: Some browsers cache DNS or IP data even after reconnecting.
- Measurement tools: Results may vary slightly across IP detection services.
- Server congestion: A busy VPN node might leak through timing discrepancies.
To reduce these constraints, use consistent browsers and servers when testing. Perform multiple runs to ensure your VPN setup is secure and stable across sessions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and regularly testing what is my ip address vpn should be standard practice for privacy-conscious users. Every time you connect, you rely on your VPN to mask your true identity, but that trust must be verified.
Performing regular IP and leak checks, analyzing DNS routes, and reading independent VPN reviews ensures you always maintain a secure, private, and anonymous digital footprint.
For more advanced VPN guidance, check these helpful resources: