Understanding how VPNs interact with wired connections is a frequent concern among IT administrators and power users. In this guide, we’ll clarify exactly does vpn work with ethernet, explain how it functions, and provide setup insights grounded in network engineering principles.
Before we dive in, remember that a point to point vpn is also known as a site-to-site VPN — a concept that helps contextualize how VPNs encapsulate traffic over any medium, including Ethernet.
Sitemap-Friendly Question List
- Does VPN work with Ethernet?
- Why choose Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi for VPN?
- What technical issues can prevent VPN from working over Ethernet?
- How to configure VPN on Ethernet step by step?
- How to share a VPN connection through Ethernet?
- How to verify and optimize VPN performance on wired links?
Does VPN Work With Ethernet?
Yes — a VPN functions perfectly over an Ethernet cable. VPNs operate at Layer 3 (the IP layer), while Ethernet exists at Layer 2 of the OSI model. Because a VPN encrypts and tunnels IP packets, the underlying medium — wired, wireless, fiber — is irrelevant.
According to Wikipedia on Virtual Private Networks, VPNs “extend private networks across public infrastructure through encryption and tunneling protocols,” meaning they work identically whether your computer connects via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
In short: a wired connection doesn’t bypass or interfere with VPN encryption; it simply provides a more stable transport medium.
Why Use Ethernet for a VPN Connection?
Stable throughput and lower latency
Ethernet delivers consistent bandwidth and lower packet loss compared to Wi-Fi. For latency-sensitive applications — streaming, VoIP, gaming, or remote desktop — this ensures a smoother encrypted session.
For example, when testing under identical VPN servers, Ethernet often shows 10–20 ms less jitter than 5 GHz Wi-Fi connections.
Reduced local interception risk
While both mediums are encrypted end-to-end once VPN is active, Wi-Fi remains more exposed to local attacks such as rogue AP spoofing or packet sniffing. Ethernet is confined to the physical network, minimizing nearby interception risks.
Ideal for large-scale or office environments
Corporate administrators often prefer wired VPN connections for reliability in site-to-site IPsec tunnels or workstation security policies. Learn how enterprise-grade devices handle multiple tunnels in this related guide:
what is a vpn concentrator — Secure Multi-Tunnel VPN Device.
What Technical Problems Can Stop VPN from Working Over Ethernet?
Even though a VPN works regardless of medium, several system-level conflicts may cause Ethernet-specific failures.
Interface metrics and routing priority
Operating systems assign metrics to interfaces (lower = higher priority). If Wi-Fi retains a higher routing priority, packets may exit through it instead of the VPN tunnel. Adjusting interface metrics in Windows (netsh interface ipv4 set interface <id> metric=<value>) or macOS resolves this.
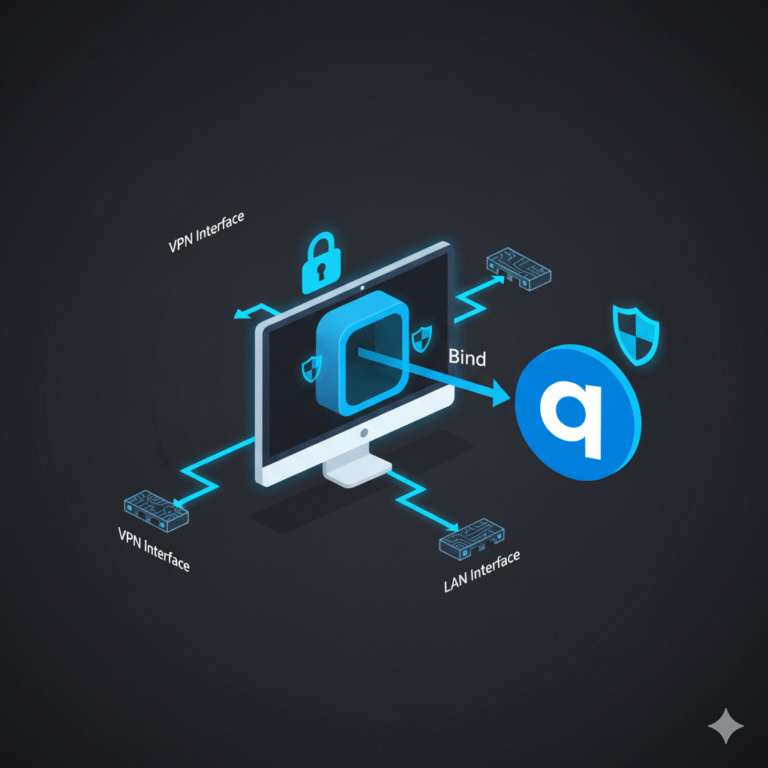
For more advanced routing use cases, such as binding specific applications or torrent clients to the VPN adapter, see
how to bind qbittorrent to vpn for secure torrenting.
VPN client software limitations
Certain clients, notably older enterprise VPNs, cache adapter IDs during installation. If Ethernet uses a different adapter index than Wi-Fi, the VPN may fail to attach. Updating or reinstalling the client typically fixes this.
Split-tunneling misconfiguration
When partial routing (split tunneling) is enabled, Ethernet subnets may inadvertently remain outside the encrypted tunnel. Validate route tables with route print or ip route show. For a deeper explanation of multi-route tunneling concepts, refer to
which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site vpn.
Sharing VPN over Ethernet
If you attempt to share your VPN connection from one PC to another through an Ethernet cable (ICS – Internet Connection Sharing), you’ll need to enable sharing on the VPN adapter itself.
- Run VPN first.
- Open Network Connections → VPN adapter Properties → Sharing tab.
- Allow “Other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection.”
- Select the wired adapter.
Microsoft’s documentation on Internet Connection Sharing outlines the general principle.
How to Configure VPN Over Ethernet (Example: Windows / WireGuard)
- Install the VPN client — choose a modern protocol such as WireGuard for low overhead.
- Ensure the Ethernet link is active — verify with
ipconfigthat a valid IPv4 address exists. - Launch the VPN and confirm a virtual adapter (e.g.,
wg0orTAP-Windows Adapter V9) appears. - Adjust routing metrics so the VPN’s virtual adapter outranks Ethernet in priority.
- Validate full-tunnel routing:
0.0.0.0/0 → VPN-Gateway 192.168.1.0/24 → Ethernet-Gateway - Test connectivity: ping an external IP to confirm encrypted routing.
For users interested in evaluating client performance differences, check
AirVPN vs NordVPN — Which VPN Offers Better Security & Speed?
and vendor-neutral benchmarks such as TechRadar’s VPN Performance Comparison.
How to Share and Extend a VPN Over Ethernet
Sharing your VPN connection through Ethernet allows a secondary device (for example, a smart TV, console, or another PC) to benefit from the encrypted tunnel without running its own VPN client. This is common in home setups and testing labs.
Windows Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
- Connect your PC to the VPN first.
- Open Control Panel → Network Connections.
- Right-click the VPN adapter → Properties → Sharing tab.
- Enable “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection.”
- Choose the Ethernet adapter.
- The client device connected by cable should receive an IP from your PC’s DHCP (typically 192.168.137.x).
To troubleshoot ICS or routing issues, Microsoft’s official ICS documentation provides technical insights.
macOS and Linux equivalents
- On macOS, open System Preferences → Sharing → Internet Sharing, select the VPN interface as the source and Ethernet as the output.
- On Linux, use
iptablesforwarding rules ornm-connection-editorto enable sharing manually.
If your shared VPN connection experiences slow speeds, see
Does Using a VPN Help with Ping? Find Out Now
to understand latency factors in VPN routing.
How to Verify Performance and Security on Wired VPN Links
Measuring speed and packet stability
Tools such as iperf3 or PingPlotter help visualize latency variation and loss rate. Wired connections typically exhibit under 1% packet loss and lower jitter than Wi-Fi.
Validating encryption and routing
Run:
tracert 8.8.8.8
or
curl ifconfig.io
The IP should show the VPN server, confirming that Ethernet traffic is tunneled correctly.
For additional context about encrypted protocols, see
Is DNSCrypt an Alternative to VPN? Explained Simply.
Common Scenarios Where Ethernet VPN Fails
Corporate firewalls blocking VPN protocols
Some enterprise networks block UDP ports (e.g., 51820 for WireGuard, 1194 for OpenVPN). Switching to TCP or port 443 often resolves this.
Outdated NIC drivers or hardware offloading
Disable “Large Send Offload (LSO)” and “Checksum Offload” in Ethernet adapter settings if encryption stalls occur.
ISP restrictions
Certain ISPs throttle or inspect VPN traffic regardless of connection type. Bypassing deep packet inspection (DPI) can be done by switching to stealth protocols like Obfsproxy or using Surfshark review 2025 – Fast, Secure & Unlimited Devices? which support obfuscation.
How Ethernet VPNs Fit in Broader Network Design
VPNs over Ethernet are foundational to LAN-to-LAN or site-to-site connections, commonly built using IPsec or SSL-based tunnels. In corporate environments, these are managed by dedicated appliances or concentrators.
For an overview, read what is a vpn concentrator — Secure Multi-Tunnel VPN Device.
If you’re exploring which commercial VPN suits your infrastructure, compare detailed performance data in
NordVPN Review: Top Features & Performance in 2025
and ExpressVPN Review – Tested in 2025: Speed, Privacy & Ease.
Conclusion
To summarize — does vpn work with ethernet? Absolutely. The VPN’s functionality remains identical whether your device uses a wired or wireless medium, because the encryption operates at the IP layer. Ethernet merely provides a faster and more stable foundation.
When configured correctly, Ethernet VPN links ensure consistent throughput, lower latency, and enhanced reliability for sensitive applications like VoIP, remote administration, and streaming.
Just remember: VPN performance depends not only on your local hardware but also on the chosen provider and server location. Explore our full VPN insights such as
: can i run a vpn with hughesnet – Speed & Compatibility Guide
and can a vpn bypass an ip ban?
for complementary topics on network performance and access.
And, as mentioned earlier, a point to point vpn is also known as a site-to-site VPN — proving again that VPNs transcend medium type, focusing entirely on secure, encapsulated communication.
FAQ Section
Q1: Does a VPN protect Ethernet traffic automatically?
Yes. Once connected, all IP packets — wired or wireless — are encrypted through the VPN tunnel unless excluded via split tunneling.
Q2: Why is my VPN not connecting when using Ethernet?
Common reasons include incorrect routing metrics, outdated NIC drivers, or firewall restrictions blocking VPN ports.
Q3: Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi when using a VPN?
Usually yes. Ethernet’s stability and reduced interference yield lower latency and higher throughput.
Q4: Can I share my Ethernet VPN with another device?
Yes, via Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) or router-based VPN configuration, allowing multiple devices to use the same encrypted link.
Q5: Do I need special hardware for Ethernet VPNs?
No. Any NIC supporting TCP/IP works; however, enterprise setups often use dedicated concentrators for scalability.
Q6: Does Ethernet VPN reduce ping in games?
Often — wired VPN links lower jitter and packet loss compared to Wi-Fi, improving gaming responsiveness.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Does a VPN protect Ethernet traffic automatically?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Yes. Once connected, all IP packets — wired or wireless — are encrypted through the VPN tunnel unless excluded via split tunneling."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Why is my VPN not connecting when using Ethernet?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Common reasons include incorrect routing metrics, outdated NIC drivers, or firewall restrictions blocking VPN ports."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi when using a VPN?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Usually yes. Ethernet’s stability and reduced interference yield lower latency and higher throughput."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Can I share my Ethernet VPN with another device?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Yes, via Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) or router-based VPN configuration, allowing multiple devices to use the same encrypted link."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Do I need special hardware for Ethernet VPNs?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "No. Any NIC supporting TCP/IP works; however, enterprise setups often use dedicated concentrators for scalability."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Does Ethernet VPN reduce ping in games?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Often — wired VPN links lower jitter and packet loss compared to Wi-Fi, improving gaming responsiveness."
}
}
]
}